Introduction
UV light is commonly used in insect killers, also known as bug zappers, to attract and eliminate flying insects. The use of UV light in bug zappers has been a popular method for decades, offering an environmentally-friendly alternative to chemical insecticides. However, concerns have been raised about the potential harm that UV light from bug zappers may pose to humans and the environment. In this blog, we will delve into the topic and explore whether the UV light used in insect killers is truly harmful.
Table of Contents
Is UV light from Bug Zappers harmful?


Generally, the UV light used in bug zappers is typically generated by special bulbs that are designed not to be harmful to humans. Under normal circumstances, the intensity of the UV light is not strong enough to cause damage to the eyes. In our another blog“Are Electronic Insect Killer safe for humans and pets?”,you can find more assurance of the UV light safety of our Insect Killers.
However, it is crucial to ensure that the correct type of bulb is used, as using the wrong bulb can expose people to potential dangers. For instance, many years ago we met a customer at Canton fair who told us that he bought cheap insect killers from another factory and got his clients’ eyes hurt.
Therefore, it is essential to select high-quality models that emit appropriate and safe levels of UV light is paramount. Meanwhile,be cautious and avoid looking directly into a bug zapper for an extended period, as this will make you feel unconformtable like when you stare at the sun.
Here are also some tips for you to ensure safer usage of UV light Insect Killers:
- Understanding UV Light Intensity: UV light emitted by bug zappers is typically of low intensity, which means it’s not strong enough to cause harm to humans under normal conditions. However, it is essential to avoid using bug zappers that emit extremely intense UV light, as this can be hazardous to human health. Choosing bug zappers from reputable brands and manufacturers ensures that they meet safety standards and emit appropriate UV light levels.
- Responsible Placement: Proper placement of bug zappers is crucial to minimize potential risks. Install bug zappers in areas away from where people usually gather or sit. Placing them closer to insect breeding areas, such as gardens or yards, can be more effective without increasing the risk of human exposure.
- Avoid Direct Staring: While bug zappers can be mesmerizing to watch, it’s important not to stare directly at the UV light for extended periods. Prolonged direct exposure to UV light, even from low-intensity sources, may cause discomfort and eye strain.
- Protective Barriers: Reputable bug zapper models come with protective barriers, preventing accidental contact with the electrified grid or UV light source. Regularly check and maintain these barriers to ensure their effectiveness.
- Correct Bulb Replacement: Always use the appropriate replacement bulbs specified by the manufacturer to ensure the bug zapper functions as intended. Incorrect bulb types may lead to inefficiency or potential hazards.
In addition, we would like to share with you more knowledge of Insect Killer light, hope it can help you to know it more, use it correctly, and even select a high-quality UV light Bug Zapper.
What UV light is generally used in Bug Zappers?
Insect killers, commonly known as bug zappers, use ultraviolet (UV) light to attract and trap insects. Specifically, they emit UV-A light(neither UV-B light nor UV-C light), which falls within the ultraviolet spectrum with wavelengths ranging from 315 to 400 nanometers. This particular wavelength is proven to be safe and highly attractive to many flying insects, including mosquitoes, flies, moths, and other pests. When these insects are drawn towards the UV-A light source, they come into contact with an electrified grid, resulting in their quick elimination. The use of UV-A light has proven to be an effective and eco-friendly method for controlling flying insect populations in outdoor areas.
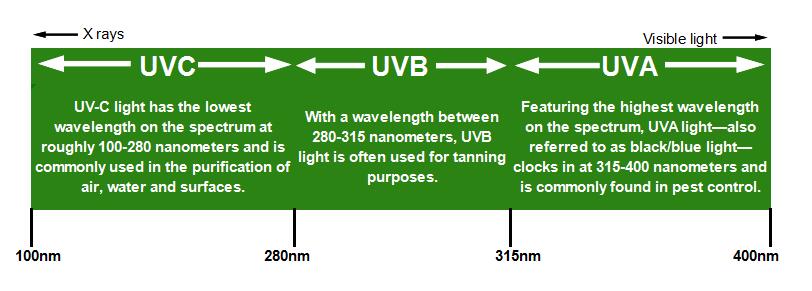
How many years is the use of UV light in Bug Zappers?
The use of UV-A light in Bug Zappers has been around for several decades. The technology of using UV-A light to attract and trap insects dates back to the early 20th century. The first commercial bug zapper was patented in 1934 by William F. Folmer and Harrison L. Chapin. Since then, bug zappers utilizing UV-A light have become increasingly popular and widely used as an effective method to control flying insect populations.
Over the years, bug zapper designs and technologies have evolved, but the fundamental concept of using UV-A light to attract insects has remained consistent. UV-A light, which falls within the ultraviolet spectrum with wavelengths ranging from 315 to 400 nanometers, is particularly attractive to many flying insects, including mosquitoes, moths, flies, and other pests.
UV-A light’s effectiveness in luring insects towards bug zappers has led to its continued use in insect control devices, making bug zappers a common sight in outdoor spaces like gardens, patios, and camping areas. The technology has proven to be an eco-friendly alternative to chemical insecticides for reducing insect populations in certain settings.
In conclusion, the use of UV-A light in insect killers has a long history, and it remains a popular and effective method for attracting and eliminating flying insects, providing people with a more comfortable and enjoyable indoor and outdoor experience, and you can trust the general safety of UV light from Bug Zapper.
Safety Considerations for Humans
- UV Radiation: UV light falls under the category of non-ionizing radiation. Exposure to excessive UV radiation can lead to skin damage, including sunburn and an increased risk of skin cancer. However, the UV light emitted by bug zappers is typically within safe limits for human exposure.
- Eye Irritation: Direct exposure to UV light can cause eye irritation, similar to the effects of staring at the sun. Placing bug zappers away from areas where people gather can help reduce the risk of eye irritation.
- Electric Shock Hazard: While modern bug zappers are designed with safety features to prevent accidental contact with the electrified grid, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and keep the device out of reach of children and pets.
Safety Considerations for Pets
- Sensitivity to Light: Some pets, particularly cats and birds, have higher sensitivity to light. Excessive exposure to UV light from bug zappers may cause discomfort or stress in sensitive pets. Observing their behavior around the device can help assess any adverse effects.
- Potential for Injury: Small pets, such as kittens or puppies, may be curious and inadvertently touch the electrified grid, leading to a risk of injury. Supervision and placing the bug zapper in a secure location can mitigate this risk.
Choosing a Safe UV Light Insect Killer
To ensure the safety of humans and pets, consider the following when selecting a UV light insect killer:
- Quality and Certification: Opt for bug zappers that comply with safety standards, such as the EN 60335-2-59 in Europe or other relevant safety certifications in your region.
- Protective Features: Look for bug zappers with protective barriers or screens to prevent accidental contact with the electrified grid.
- Placement: Install the bug zapper in areas away from where people and pets frequently gather, reducing direct exposure to UV light.
Electronic Insect Killer has been our only business, and we GLEECON have been focused on its safety and its effectiveness. Our all UV-A lamps are tested with the appliances, and proven to be safe for the users. Following you can find our CE marking of our some UV-A lamps for your reference firstly. Welcome you to contact us to explore the more safety assurance of our UV light Insect Killer ,or share with us your doubt. We are more than happy to answer your any questions.


Conclusion
UV light insect killers can be effective tools for controlling flying insects in homes and outdoor spaces. While these devices emit UV light, which can potentially cause skin and eye irritation, modern bug zappers are generally safe for human use under normal conditions. It’s essential to choose a quality bug zapper with appropriate safety features and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and use.
When it comes to pets, it’s crucial to be mindful of their sensitivity to light and supervise their behavior around the device. By taking necessary precautions and making informed decisions, you can enjoy the benefits of a bug-free environment while ensuring the safety and well-being of both humans and pets.








